Answer
They used asbestos-based fake snow. At the time, asbestos fibers were a popular material for fake snow. Asbestos was used as fake snow until the beginning of World War II, when it was needed on ships.
How did they film the poppy field scene in Wizard of Oz?

Soundskrit uses a radically new transducer design to sense the direction of sound with incredible precision.
We have spent the last 20 years trying to use non-directional microphones to get directionality. Why not build the directionality into the hardware from the beginning?
Soundskrit has rebuilt the MEMS microphone from the ground up with directionality in mind, bringing unparalleled performance to the world of audio.
1. A Completely New Mechanical Design
We changed how the MEMS element looks so it would move closely in sync with the surrounding air. Since a sound wave is simply a displacement of air, our MEMS elements closely sense any incoming sound.
2. A New Method Of Transduction
Traditional methods of capacitive sensing typically impede the motion of the MEMS element. We use a new capacitive readout architecture that leaves the MEMS element unobstructed, free to move with the surrounding air.
3. A Package Built for Directionality
We optimized every detail of our microphone package in order to preserve directionality across all frequencies in the audio spectrum. Our microphones are incredibly small—the smallest directional microphones on the market!
Leveraging the Power of AI
Leveraging the Power of AI
We have co-designed the hardware and software to provide the greatest level of performance. We’ve combined a deep level of understanding of the acoustics around directional microphones with some of the latest advancements in neural networks to develop in-house AI to unlock the full potential of our new microphones. Whether its eliminating background noise and reverb, tracking multiple speakers around a room, or detecting the distance of a sound from the microphone, our AI brings a pallet of new features to end customers.
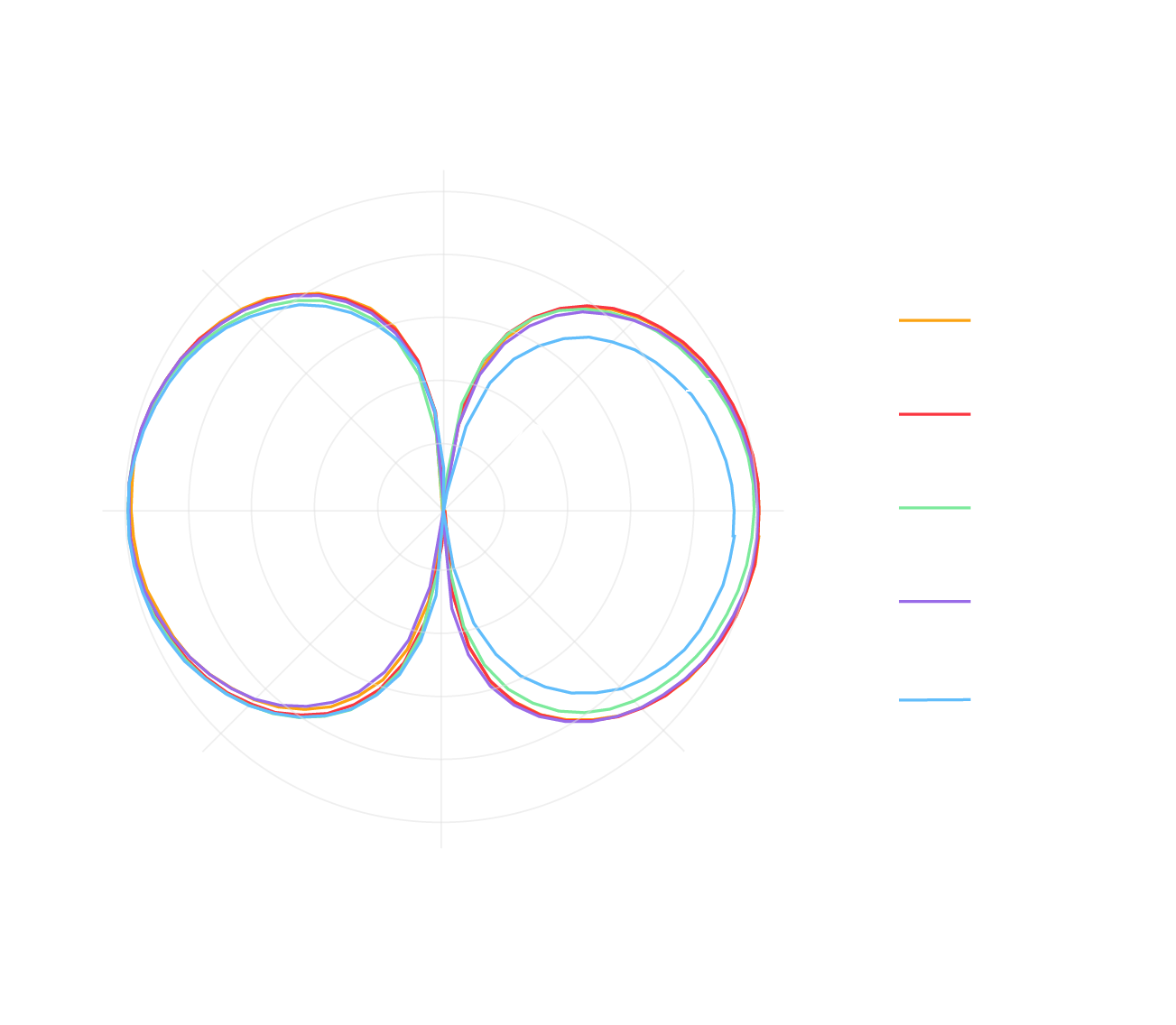
Check out the performance of our technology for yourself. Whether using the raw output from a single microphone alone or recombining multiple microphones with our proprietary AI, Soundskrit brings an impressive level of performance. We have a solution to meet any need.
Fun Fact
Chewbacca was inspired by which real life figure?
Demo Kits
Come try out Soundskrit’s technology for yourself by with our demo kits built to help you explore using our technology across a variety of your products.

Demo Kits
Come try out Soundskrit’s technology for yourself. Our easy-to-use demo kits walk you through various ways to configure our microphones for your products.
Applications
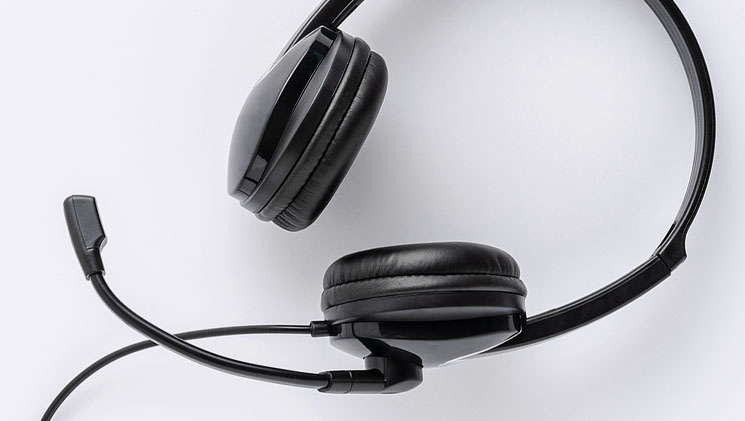
Conferencing Devices
Everyone on the speaker phone should sound great no matter where they sit around the table.
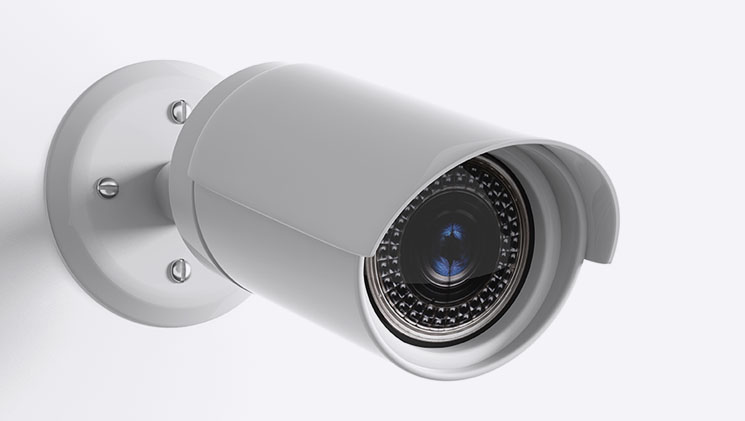
Home Security Cameras
Security cameras that can hear what’s going on even before it sees it.
Application Notes
Designing Linear Arrays with Directional MEMS Microphones
AN-210 examines how arrays designed with directional microphones differ from those using omnidirectional microphones.
Attributes of Directional MEMS Microphones
AN-110 walks through key attributes of Soundskrit's directional microphones such as directionality, SNR, acoustic path length, and more.
Comparing Omnidirectional and Directional MEMS Microphones
AN-100 explains the key differences between directional and omnidirectional MEMS microphones.